Deploy Container Image
In this section, we will introduce how to deploy a container-based application with KubeVela. The guide will run the whole process with UI console as it's quite the same with the quick start if you're using CLI.
Before starting
- Containerize your business, you need a container image within your image registry that can be accessed by KubeVela.
- Make sure you have VelaUX addon enabled.
vela addon enable velaux
Creating an application
Enter the page of Application on the left, and click New Application to create. Pick your name, alias, and description; Select type of webservice; Decide your environment, Default environment is already available in the first place. You could also enter the page of Environments to set up new.
Click Next Step so to the configuration page. You need to set up the Image address and resources limit. If you want to set up a command for the image, open up the row CMD.
If you want to deploy the private image, please create the registry integration configuration. refer to: Image registry configuration
After inputting the Image address, the system will load the Image info from the registry. If the image belongs to the private image registry, the Secret field will be automatically assigned values.
You could refer to their information to configure the Service Ports and Persistent Storage.
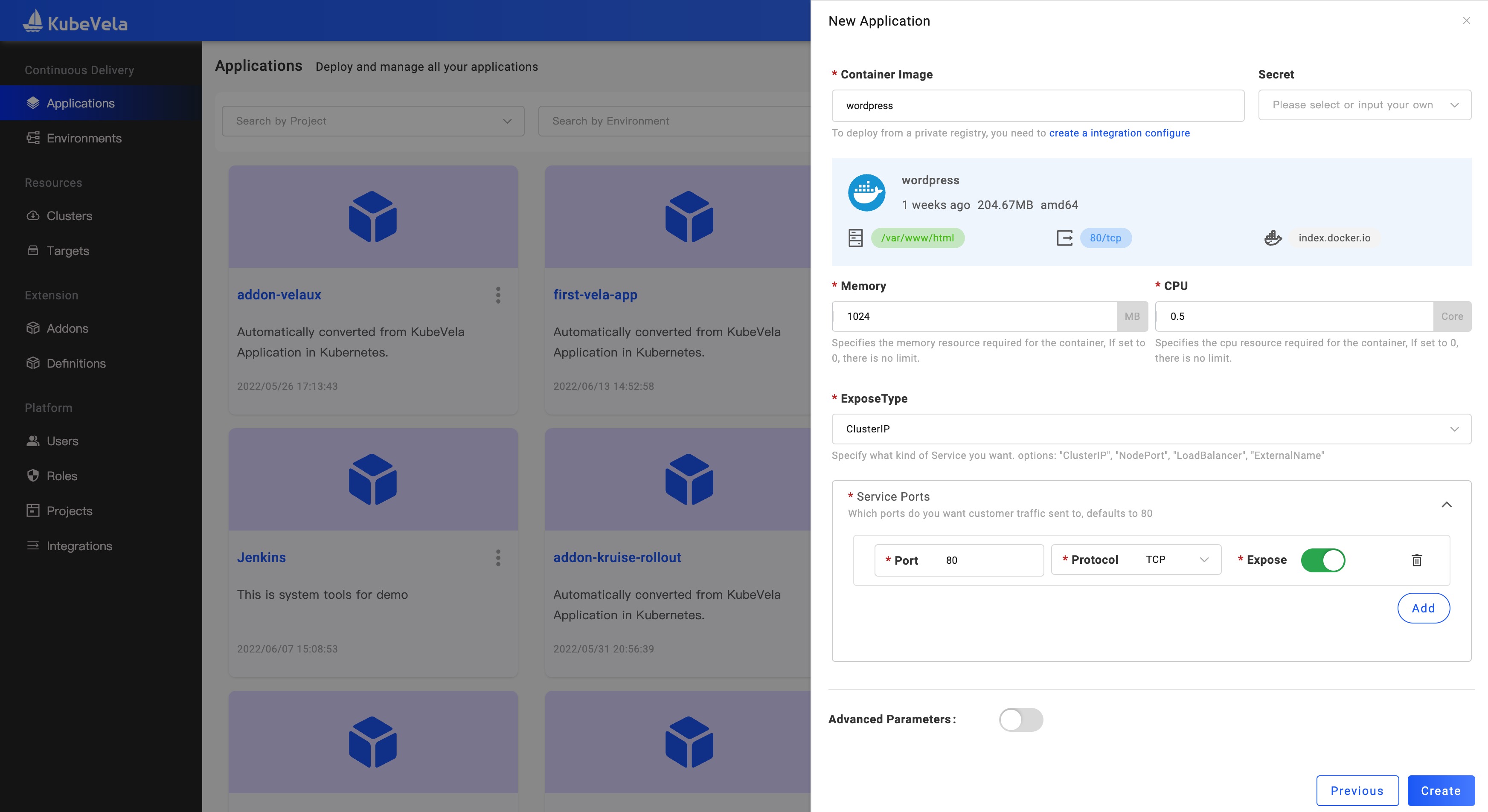
Done by clicking Create and then we enter the management page.
Deploying the application
Click the Deploy button on the upper right and select a workflow. Note that each Environment of the application has its workflow. On the right of the Baseline Config tab is the environments. Check out the status of the environment and its instance information as you wish.
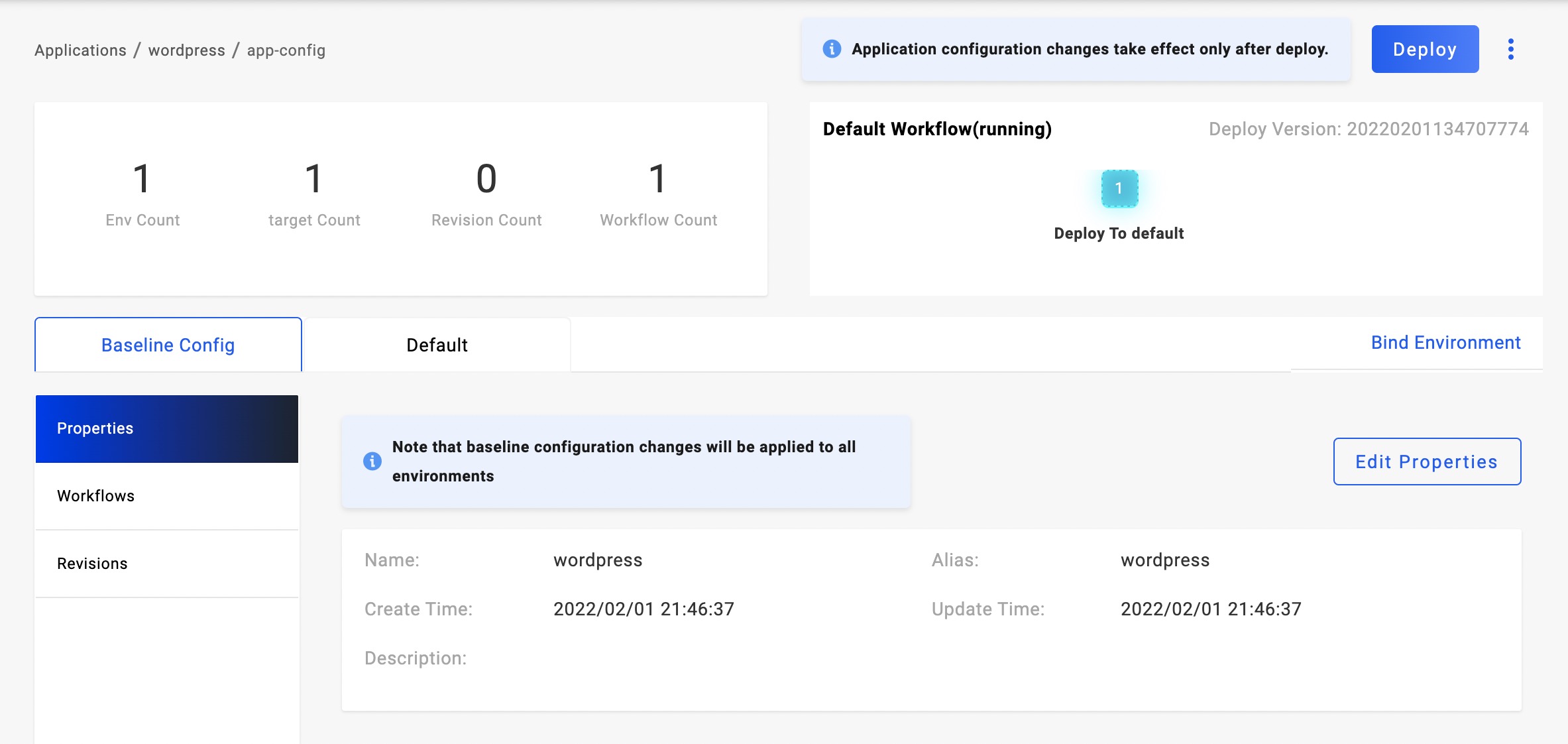
When it has several targets in this environment, you may find them all in the Instances list. If you want to look at the process of application deployment, click Check the details to reveal.
In the Instances list, you may find some of them are in pending status. Click + in the beginning to figure out the reason in more detail.
Update image
After the first deployment, our business keeps evolving and the following updates come along.
Click Baseline Config and you can see the all components. Then click the component name and open the configuration page, you can update your latest requirements for image, version, and environment variable.
Update replicas
If your business requires more than one replica, enter the Properties page. By default, The component has a Set Replicas trait. Click it so that you can update the replicas.
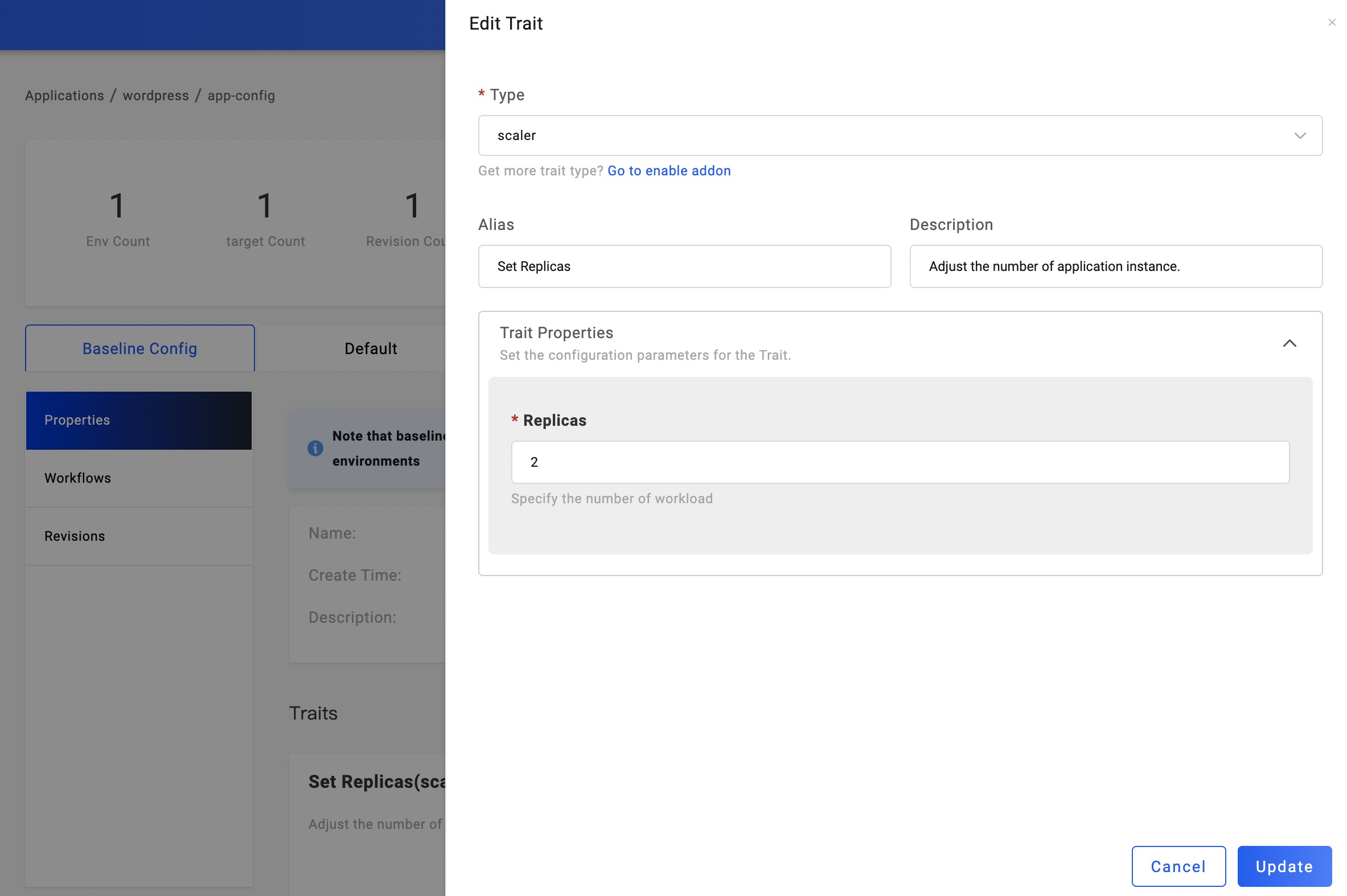
Upgrading the application
By twos steps as above, it is still in a draft state, we need to click the deployment button again to complete the upgrade of the application.
Application recycling and deletion
If you need to delete the application after testing, you need to recycle all the deployed environments first. Click the environment name to enter the environment instance list, and click the Recycle button to recycle the deployment of the application in that environment. After it's done, the application in this environment rolls back as an undeployed one.
After all of the environments have been recycled, the application can be deleted. Currently, the entry for application deletion is on the application list page. Back to the application list page, mouse on the menu icon on the right side of the application name, and click the Remove option.
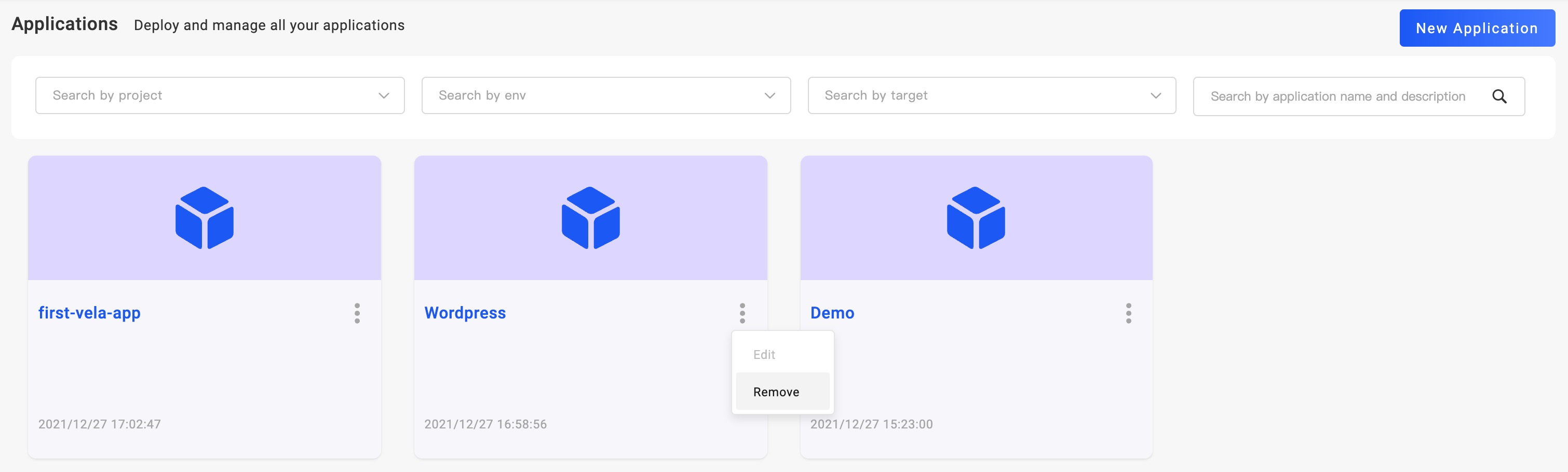
At this point, you have basically mastered the deployment method of Docker image.
You can refer to how to manage applications to learn the details about the UI console operations.
Deploy via CLI
You also can deploy the application via CLI.
cat <<EOF | vela up -f -
# YAML begins
apiVersion: core.oam.dev/v1beta1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: webservice-app
spec:
components:
- name: frontend
type: webservice
properties:
image: oamdev/testapp:v1
cmd: ["node", "server.js"]
ports:
- port: 8080
expose: true
exposeType: NodePort
cpu: "0.5"
memory: "512Mi"
traits:
- type: scaler
properties:
replicas: 1
# YAML ends
EOF
The application created by CLI will be synced to UI automatically.
You can also save the YAML file as webservice-app.yaml and use the vela up -f webservice-app.yaml command to deploy.
Next, check the deployment status of the application through vela status webservice-app
About:
Name: test-app
Namespace: default
Created at: 2022-04-21 12:03:42 +0800 CST
Status: running
...snip...
Services:
- Name: frontend
Cluster: local Namespace: default
Type: webservice
Healthy Ready:1/1
Traits:
✅ scaler
Depending on how you install KubeVela, you can choose the way to access the endpoint.
- Standalone Local
- Standalone Remote
- Kubernetes
You can access the endpoint by port-forward command:
vela port-forward webservice-app -n default 8080:8080
This command will open a browser automatically. Or you could access the endpoint by http://127.0.0.1:8080 in your browser.
Since we have install KubeVela in a remote server with accessible IP address, you can check the application endpoint using vela status --endpoint. This command can detect multiple kinds of endpoints.
In this case, it is a NodePort Service under the hood. You can access the endpoint listed in the output.
vela status webservice-app --endpoint
expected output
I0816 21:20:08.536617 59163 utils.go:156] find cluster gateway service vela-system/kubevela-cluster-gateway-service:9443
Please access webservice-app from the following endpoints:
+---------+-----------+--------------------------+----------------------------+-------+
| CLUSTER | COMPONENT | REF(KIND/NAMESPACE/NAME) | ENDPOINT | INNER |
+---------+-----------+--------------------------+----------------------------+-------+
| local | frontend | Service/default/frontend | http://182.92.178.219:30128 | false |
+---------+-----------+--------------------------+----------------------------+-------+
If you are using a cloud server, please open this port in secure group.
You can check the application endpoint using vela status --endpoint. This command can detect multiple kinds of endpoints.
In this case, it is a NodePort Service under the hood. You can access the endpoint listed in the output.
vela status webservice-app --endpoint
expected output
I0816 21:20:08.536617 59163 utils.go:156] find cluster gateway service vela-system/kubevela-cluster-gateway-service:9443
Please access webservice-app from the following endpoints:
+---------+-----------+--------------------------+----------------------------+-------+
| CLUSTER | COMPONENT | REF(KIND/NAMESPACE/NAME) | ENDPOINT | INNER |
+---------+-----------+--------------------------+----------------------------+-------+
| local | frontend | Service/default/frontend | http://182.92.178.219:30128 | false |
+---------+-----------+--------------------------+----------------------------+-------+
The output from the preceding command shows that the NodePort service is exposed externally on the port (30128) of the available cluster node. Before you access NodeIP:NodePort(182.92.178.219:30128) from outside the cluster, you must set the security group of the nodes to allow incoming traffic. You should allow incoming traffic through the port (30128).
Now, you have finished learning the basic delivery for container images. Then, you could:
- Refer to webservice details to know usage of full fields.
- Refer to trait reference to know which traits can be used for webservice.
- Refer to multi-cluster delivery to know how to deploy container image into hybrid environment and multi-clusters.