UX of Definition
VelaUX uses the UI-Schema specification to customize UI elements of components, workflow steps, and operation and maintenance feature resources, in the case of variable input parameters, to achieve a more native UI experience.
At present, the UI-Schema specification mainly acts on the data input side and will be extended to the data visualization side in the future.
How UI-Schema works
The components, workflow steps, and operation and maintenance feature types with different UI-Schema working principles are defined through CUE, which we call XDefinition, and almost every definition includes the definition of input parameters. for example:
scaler: {
type: "trait"
annotations: {}
labels: {}
description: "Manually scale K8s pod for your workload which follows the pod spec in path 'spec.template'."
attributes: {
podDisruptive: false
appliesToWorkloads: ["*"]
}
}
template: {
parameter: {
// +usage=Specify the number of workload
replicas: *1 | int
}
// +patchStrategy=retainKeys
patch: spec: replicas: parameter.replicas
}
In the above example, the user input parameter is replicas.
In the UI we want the user to be able to set the number of replicas via a number input form.
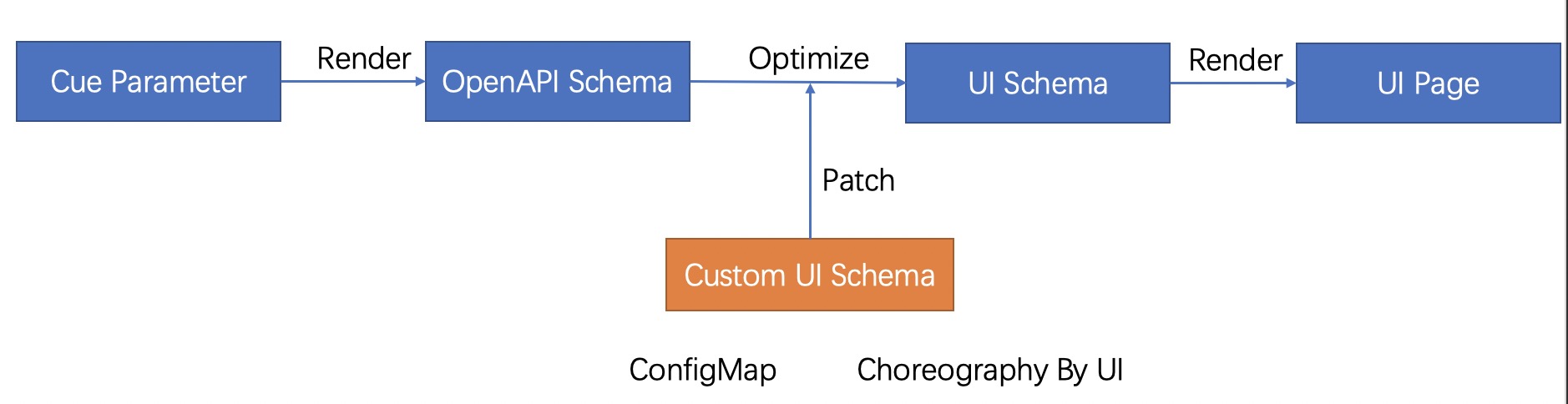
Its workflow is in the figure above. The API Schema is generated through the defined CUE, and then the default UI Schema is generated through the API Schema. If there is a custom UI Schema, the default configuration is patched with the custom configuration. The UI renders the front-end page based on the final UI Schema.
The spec are as follows:
- jsonKey: string The field name
label: string The show name in UI
description: string The help info in UI
uiType: string The react component type in UI
sort: int The sort number
disabled: bool Disable this field.
style:
colSpan: int Defines the number of grids for the form, with 24 representing 100% width.
conditions: Control whether fields are enabled or disabled by certain conditions.
- jsonKey: string Specifies the path of the field, support the peer and subordinate fields.
op: == | != | in
value: any Specifies the expected value.
action: enable|disable
validate: The value validate rule, It must be defined as a whole.
defaultValue: any The default values.
required: bool
max: int The max value for number.
min: int The min value for number.
maxLength: int The max length for string.
minLength: int The min length for string.
pattern: string
options: Optional, for select forms
- label: string
value: string
immutable: bool Set the immutable is true, indicates that the parameter cannot be changed.
subParameters:
- jsonKey: string
...
Supported react component types
Basic form
- Input
- Number
- Select
- Switch
- Radio
- Password
Business form
- Ignore: There are subordinate fields, and the current field is not displayed.
- SecretSelect: Load the secret list to assist user selection
- SecretKeySelect: Load the secret key list by the secret name of the user selected to assist user selection
- CPUNumber: CPU-style number input form.
- MemoryNumber: Memory-style number input form.
- DiskNumber: Disk-style number input form.
- K8sObjectsCode: The YAML input form of Kubernetes resource.
- HelmRepoSelect: Load the helm repositories from integration configs to assist user selection.
- HelmChartSelect: Load the helm charts to assist user selection.
- HelmChartVersionSelect: Load the versions of the selected helm chart to assist user selection.
- HelmValues: Load the default values of the selected helm chart and version to assist the user to configure the custom values.
- PolicySelect: Load the policies of the current application to assist user selection.
- ImageInput: Load and show the image info by users input image name.
- CertBase64: Support users upload or input the string, automatically base64 encoded. Suitable the fields such as the certificates and keys. (Added in 1.5+)
Combination form
- KV
- Strings
- Structs
- Group: render as a titled container
Example
KubeVela store UISchema config in a ConfigMap in the same namespace with the definition object.
The default KubeVela system namespace is vela-system, the built-in capabilities and uischemas are laid there.
You can use the following command to get the ConfigMap list of Custom UISchema.
kubectl get configmap -n vela-system | grep uischema
NAME DATA AGE
addon-uischema-velaux 1 25h
component-uischema-helm 1 25h
component-uischema-k8s-objects 1 25h
component-uischema-kustomize 1 25h
component-uischema-task 1 25h
config-uischema-helm-repository 1 25h
config-uischema-image-registry 1 25h
The ConfigMap name is in the format of <your-definition-type>-uischema-<your-definition-name>, and the data key is ui-schema.
For example, we can use the following command to get the UISchema of k8s-objects which tpe is component.
kubectl get configmap -n vela-system component-uischema-k8s-objects -oyaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: component-uischema-k8s-objects
namespace: vela-system
data:
ui-schema: '[{"jsonKey":"objects","uiType":"K8sObjectsCode"}]'
For more examples, please refer to the following links:https://github.com/kubevela/catalog/tree/master/addons/velaux/schemas
How to expand
UI-Schema mainly extends front-end react components, refer to https://github.com/kubevela/velaux/tree/main/packages/velaux-ui/src/extends